
CAVITATION EROSION
This is an impact fatigue attack caused by the formation and collapse of vapour bubbles in the oil film under conditions of rapid pressure changes during the crank cycle in internal combustion engines. The harder the bearing material the greater is its resistance to Cavitation Erosion.
JOURNAL BEARINGS
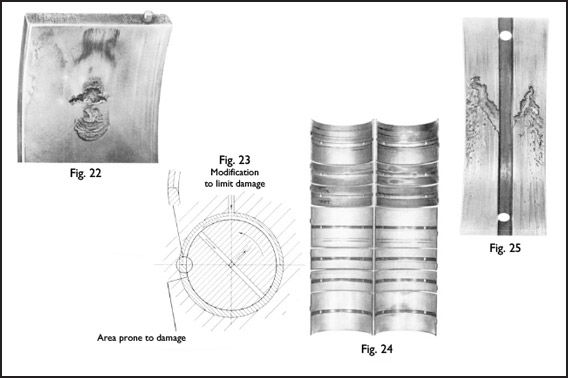
Fig. 22 - Impact cavitation erosion of ungrooved whitemetal-lined bearing occurring downstream of bearing joint face and groove in the other half.
Fig. 23 - Section through main bearing illustrating mechanism of cavitation and modification to groove to limit or reduce
damage.
Fig. 24 - Discharge cavitation erosion in unloaded half-bearing caused by rapid movement of journal in clearance space during Crank cycle.
Fig. 25 - Set of diesel engine main bearings showing cavitation erosion of soft overlay while harder tin-aluminium is unattacked.
RECOMMENDED ACTION
• Bearings may be put back into service if cavitation attack is not very severe or extensive. Investigate practicability of increasing oil feed pressure. modifying bearing groove, blending edges or contours to promote streamline flow, reducing running clearance or changing to harder bearing material.
Made with Mobirise web themes